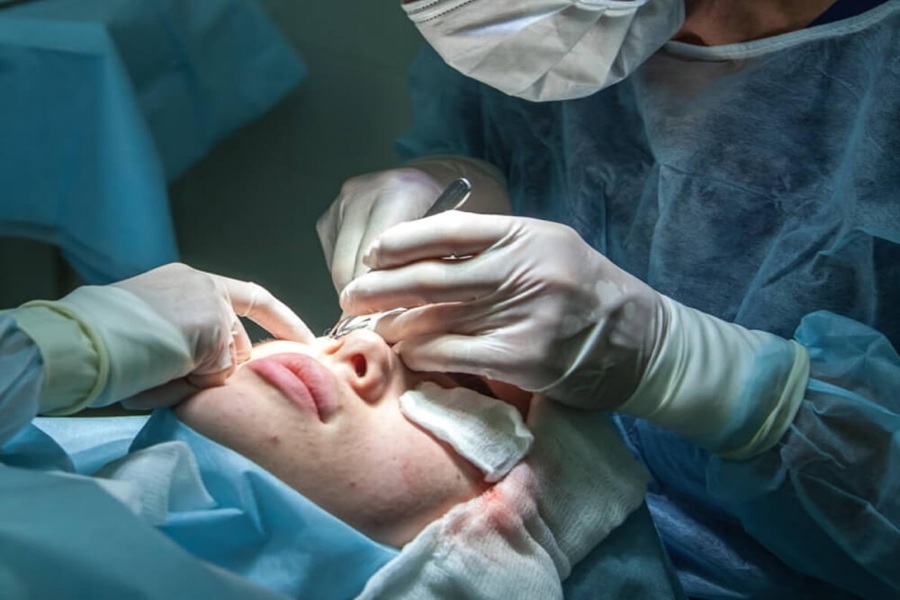
What Are Retinal Tears
A retinal tear occurs when the retina, the thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye responsible for capturing light and sending visual signals to the brain, develops a small break or crack. This condition can be caused by various factors, including aging, eye trauma, or conditions like posterior vitreous detachment (PVD).
Common Causes of Retinal Tears:
Aging: As people age, the vitreous (gel-like substance inside the eye) shrinks and pulls away from the retina. In some cases, this pull can result in a tear.
Trauma: Blunt force or injury to the eye may lead to retinal tears.
High Myopia (Nearsightedness): People with severe nearsightedness often have thinner retinas, which are more prone to tearing.
Family History: A genetic predisposition can increase your risk.
Previous Eye Surgery: Certain procedures, such as cataract surgery, could raise susceptibility to this condition.
Symptoms of Retinal Tears:
Recognizing a retinal tear early is crucial for preventing further complications like retinal detachment. Be aware of these symptoms:
- Sudden appearance of floaters (small shapes or spots moving in your vision).
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes.
- Blurred or distorted central vision.
- A gradual shadowing effect across your field of vision.
If left untreated, a retinal tear can develop into a more severe condition called retinal detachment, which may lead to permanent vision loss. This makes timely diagnosis and treatment critical.
Diagnosis:
An ophthalmologist typically diagnoses retinal tears through a comprehensive dilated eye exam using tools such as an ophthalmoscope or specialized imaging like optical coherence tomography (OCT). Early detection allows for effective treatment options.
Treatment Options:
Laser surgery is one of the most common treatments for repairing retinal tears. During this procedure: 1. A laser is used to create tiny burns around the tear. 2. These burns form scar tissue that seals the edges of the tear and prevents fluid from leaking underneath it.
Other options might include cryopexy (freezing therapy), which also helps secure the retina in place by forming scar tissue.
Understanding what retinal tears are and their associated risks is essential for maintaining optimal eye health and seeking timely care when necessary.
How Long Does It Take An Eye To Heal After Laser Surgery For A Retinal Tear
Laser surgery for a retinal tear is a commonly performed procedure designed to repair the affected part of the retina and prevent further damage, such as retinal detachment. Recovery time varies from person to person depending on factors such as the severity of the tear, individual healing responses, and adherence to post-operative care guidelines. On average, most patients experience significant recovery within two to four weeks after surgery. However, complete healing may take longer in some cases.
General Timeline for Healing
You may experience mild discomfort or soreness in the treated eye.
Vision may be blurry or distorted initially, which is normal.
Floaters or flashes of light could still be present but should diminish gradually.
Discomfort begins to lessen significantly.
Some patients notice improvement in their vision during this period, although it may not yet return to its pre-tear clarity.
The retina usually stabilizes during this phase if there are no complications.
Vision continues to improve steadily for many patients.
While most healing occurs within the first month, some individuals may see gradual improvements in vision over several months.
Factors That Impact Recovery Time
Extent and Location of the Retinal Tear: Larger or more central tears may require more time to heal compared to smaller ones located on the periphery.
Personal Health Conditions: Preexisting conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure could slow down healing.
Adherence to Aftercare Instructions: Following your ophthalmologist's advice regarding rest, medication use, and activity restrictions greatly impacts recovery speed.
Age and Lifestyle Choices: Older individuals or those with certain lifestyle habits (such as smoking) might experience slower overall healing times.
Typical Symptoms During Recovery
Blurred or fluctuating vision
Sensitivity to light
Mild inflammation
Floaters noticed after surgery
If these symptoms worsen significantly instead of improving gradually, it’s important to contact your ophthalmologist promptly for reevaluation.
By understanding what happens during each stage of recovery and what factors influence it, you can better prepare yourself for the post-surgical process while allowing your body sufficient time to heal properly.
Improving Your Recovery Time at Home
Recovering from laser surgery for a retinal tear requires careful attention to your eye health and adherence to post-operative care instructions. While the healing process varies between individuals, there are steps you can take at home to support recovery and reduce complications. Below are some practical and effective ways to encourage healing during this period.
Follow Post-Operative Instructions
After surgery, your ophthalmologist will provide specific guidelines tailored to your condition. These instructions may include:
- Prescription Eye Drops: Use them as directed to minimize inflammation or prevent infection.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or movements that may strain the eye.
- Protective Measures: Wear protective eyewear if recommended, particularly in bright sunlight or dusty environments.
Resting Your Eyes
Reducing eye strain is essential for proper healing. To accomplish this:
- Limit screen time (phones, computers, TVs) during the initial recovery phase.
- Take frequent breaks from reading or other visual tasks by following the 20-20-20 rule—look at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes.
Maintaining Proper Head Position (if Advised)
In some cases, you may be instructed to keep your head in a specific position post-surgery (e.g., face down). This positioning facilitates optimal healing depending on the location of the retinal tear.
Nutrition and Hydration for Recovery
Eating a nutrient-rich diet supports overall health and recovery. Focus on foods that promote eye health, including:
- Vitamin A: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach; helps with vision repair.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Present in fish like salmon; supports the retina's health.
- Vitamin C & E: Found in oranges, strawberries, almonds; they help reduce oxidative stress during recovery.
Drinking plenty of water also keeps tissues hydrated and promotes healing.
Avoid Irritants
Protect your eyes from potential irritants such as:
- Dusty or smoky areas.
- Chlorine pools (avoid swimming until cleared by your doctor).
- Harsh lighting—wear sunglasses when outdoors.
Creating a Comfortable Environment for Recovery
Making small adjustments at home can improve comfort during recovery: - Adjust lighting levels to avoid bright glare without straining your eyes. - Keep commonly used items within easy reach so you minimize unnecessary movements.
By following these tips closely and giving yourself time to rest properly at home, you'll create an environment conducive to efficient healing after laser surgery for a retinal tear. Regular follow-up visits with your ophthalmologist will also ensure that you’re progressing as expected throughout the recovery process.
Things You Should Focus On At Home
After undergoing laser surgery for a retinal tear, proper post-operative care at home plays a crucial role in your healing process. By following best practices during this recovery period, you can support your eye's natural healing ability and reduce the likelihood of complications. Below are several key areas to focus on while recovering at home.
Follow Post-Surgery Instructions
Your ophthalmologist will provide specific aftercare instructions tailored to your condition. These may include:
- Using prescribed eye drops: These help reduce inflammation and prevent infection. Follow the recommended schedule strictly.
- Avoiding strenuous activities: Refrain from heavy lifting, bending over, or engaging in high-impact exercises as these activities can increase pressure in the eye.
- Resting your eye: Avoid prolonged screen time or reading for extended periods during the early days of recovery to prevent strain.
Protect Your Eye
Taking precautions to shield your eye from potential harm is important:
- Wear protective eyewear: If advised, use an eye shield or glasses during sleep or in environments where debris could be present.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes: This can irritate the treated area and delay healing.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Pay attention to how your vision and overall comfort evolve during recovery. It is common to experience mild symptoms such as slight discomfort or blurry vision initially, but these should improve over time. Keeping track of any unusual changes is critical for early intervention if needed.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Supporting your body’s overall health can contribute significantly to faster healing:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly those that support eye health (e.g., Vitamin A, Vitamin C, lutein). Foods like leafy greens, carrots, and citrus fruits are excellent choices.
- Stay hydrated by drinking sufficient water throughout the day. - Avoid smoking or excessive alcohol consumption as these can hinder recovery.
Activities To Avoid During Recovery
For optimal results after surgery, there are certain activities you should avoid until cleared by your ophthalmologist: - Swimming pools or hot tubs (to prevent infection).
- Driving (especially if vision remains blurry).
- Makeup application around the eyes.
Activity | Recommended Action Timeline* |
Strenuous exercise | Wait 1–2 weeks |
Swimming | Avoid for at least 2 weeks |
Driving | Resume only when vision stabilizes |
*Always consult with your doctor about specific timelines based on individual circumstances.
Adjust Your Environment
Making small changes at home can ease strain on your eye: - Use soft lighting instead of harsh overhead lights. - Set up a comfortable space where you can rest without interruptions.
By focusing on these areas during recovery, you give yourself the best chance for successful healing while minimizing risks associated with improper care. Always keep communication lines open with your healthcare provider and address any concerns promptly to ensure a smooth recovery process.
When Should You Call Your Ophthalmologist
Post-surgery for a retinal tear, it is important to monitor your eye health and healing process closely. While laser surgery is generally successful and complications are rare, there are certain symptoms or changes that may require immediate attention from your ophthalmologist. Below are the key scenarios when you should contact your doctor.
Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Sudden or worsening vision loss: A noticeable decline in vision after surgery could indicate complications that need to be addressed quickly.
Increased floaters or flashes of light: While some floaters and flashes can be normal after surgery, a significant increase might signal further issues with the retina.
Severe eye pain: Mild discomfort is expected during recovery, but severe or persistent pain could point to an underlying concern.
Redness and swelling that worsens over time: Some redness is typical after surgery, but if it becomes excessive or is accompanied by swelling, it’s worth getting checked.
Bleeding inside the eye: Unusual bleeding inside the eye (or vitreous hemorrhage) can impair vision and may need urgent treatment.
Signs of infection: Symptoms like discharge from the eye, tenderness around the surgical area, fever, or increasing inflammation should not be ignored.
Additional Reasons To Call Your Doctor
Persistent blurry vision: Blurred vision lasting beyond what was discussed as part of normal recovery may require further evaluation.
Difficulty seeing in low light: If night vision becomes unusually challenging post-surgery, this warrants investigation.
New shadow or curtain in peripheral vision: Such changes in visual fields can be concerning signs of retinal detachment progressing further.
How To Prepare For The Call
When contacting your ophthalmologist’s office about any concerns: - Be ready to describe your symptoms in detail (e.g., when they started and how they’ve progressed). - Note any changes since the last follow-up appointment. - Mention if you've recently engaged in activities that might have strained your eyes despite recovery guidelines.
Routine Follow-Ups Are Still Important
Even if no alarming signs appear post-surgery, attending all scheduled follow-up visits with your doctor remains crucial. These appointments allow for monitoring of healing progress and early detection of potential issues before they escalate.
Monitoring changes after laser surgery for retinal tears ensures timely intervention when needed. Always trust your observations during recovery and don't hesitate to contact a professional if something feels abnormal or concerning.
When Should You Call Your Ophthalmologist
After undergoing laser surgery for a retinal tear, it is important to monitor your recovery process closely. While the procedure typically has a high success rate and most patients recover well, certain symptoms or complications may require prompt attention from your ophthalmologist. Knowing when to seek medical advice can help ensure that any potential issues are addressed early.
Sudden or Worsening Vision Changes
If you experience a sudden decrease in vision or notice blurry areas that were not present before, it’s important to notify your doctor immediately.
The appearance of new dark spots, shadows, or "curtains" in your vision could indicate further retinal complications that may require urgent treatment.
Increased Floaters or Flashes of Light
The presence of floaters (small dots or lines in your field of vision) is common after retinal surgery, but if you notice a significant increase in their frequency or size, contact your ophthalmologist.
Bright flashes of light, especially when persistent, may signal additional retinal issues that need evaluation.
Redness and Pain That Does Not Improve
Mild discomfort and redness are expected during the healing process; however, severe pain or redness that worsens over time could be a sign of infection or inflammation requiring timely medical intervention.
Signs of Infection
Pay close attention to the following symptoms:
- Persistent swelling around the eye area
- Yellowish discharge from the eye
- Fever accompanied by eye-related discomfort
These symptoms may suggest an infection and should be addressed promptly by a healthcare professional.
Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia)
While some sensitivity to light is normal after surgery, extreme discomfort when exposed to light could point to complications like increased intraocular pressure or inflammation.
Monitoring Symptoms Over Time
Symptom | Expected After Surgery? | When to Call Your Doctor |
Mild redness | Yes | If redness becomes severe or persists |
Floaters | Yes | If there is a sudden increase |
Light flashes | Rare | Persistent flashes |
Pain | Mild discomfort possible | Severe pain |
Blurry vision | Brief periods common | Sudden/worsening blurriness |
Action Steps if You Notice Concerning Symptoms
Contact your ophthalmologist as soon as possible using their emergency line if available.
Avoid activities such as heavy lifting during this period as they might exacerbate symptoms.
Follow all post-operative care instructions provided during follow-up appointments for optimal recovery outcomes.
By staying attentive to changes in your eyesight and seeking prompt care if needed, you can safeguard both the healing process and long-term health of your retina.
When Should You Call Your Ophthalmologist
While laser surgery for a retinal tear often has a positive outcome, monitoring your recovery and knowing when to seek additional medical attention is important. Some symptoms may indicate complications or the need for further evaluation by your ophthalmologist. Below are key scenarios and signs that warrant contacting your eye care professional.
Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
Increased Floaters or Flashes of Light: While these are common after a retinal tear, a sudden increase in floaters or flashes could indicate further retinal damage or detachment.
Loss of Vision: If you experience partial or total loss of vision in the treated eye, this may signal that the retina is not healing as expected.
Severe Eye Pain: Discomfort is normal after surgery, but intense pain can be a sign of complications such as increased intraocular pressure or infection.
Peripheral Vision Changes: Noticeable changes in your side vision could suggest problems with the healing process and should be addressed promptly.
New Dark Shadows in Vision: The appearance of dark spots or shadows (often referred to as a "curtain effect") could indicate retinal detachment, which requires immediate attention.
Regular Follow-Ups
Even if you do not experience any concerning symptoms, it’s essential to attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your ophthalmologist. These visits allow them to monitor the progress of your healing and detect any potential issues early.
During these visits, your doctor will: - Conduct a dilated eye exam to assess the retina. - Check for signs of infection or inflammation. - Measure intraocular pressure. - Review any symptoms you may have experienced since surgery.
Additional Signs To Report
Sometimes less urgent symptoms can still interfere with recovery and should be discussed with an eye care provider at your next appointment: - Persistent blurry vision beyond the expected recovery timeline. - Sensitivity to light that does not improve over time. - Feeling like there is something in your eye (foreign body sensation) well after surgery.
How To Contact Your Ophthalmologist
Make sure you have clear instructions on how to reach out to your ophthalmologist in case of emergencies. Many clinics provide after-hours contact information as part of their postoperative care guidelines. If you're unsure about whether something is serious, it's always better to call for clarification rather than waiting.
Being proactive about recognizing potential complications and staying consistent with follow-up care are crucial steps in achieving a smooth recovery from laser surgery for retinal tears.









